Vitamin B rich foods for vegetarians

Did you know that your everyday foods can be a wonderful source of vitamin B? every vegans getting enough vitamin B from food. That’s because many different types of foods contain this essential vitamin, including leafy greens, sunflower seeds and nuts.
Vitamin B is one of the key micronutrients that aid in keeping your body healthy and performing at its best. These little vitamins play an important role in maintaining normal metabolism, brain function and red blood cell production. B Vitamers are also essential for growth and development throughout the life cycle ( fetus , infancy , childhood , adulthood ).
In this blog post, we will explore the importance of including plant-based sources of vitamin B in your diet, as well as some delicious options that you can add to your meals and snacks to increase your intake.
Adding vitamin B in your diet not only helps you achieve better overall health but also helps you look younger as well as prevent various diseases that are caused by a deficiency of this important nutrient such as scurvy, brittle hair, brittle nails, dry skin, easy bruising, poor night vision and poor memory.
In this article, we will examine some of the best plant sources of vitamin B (B1, B2, B3 , B5 , B6 , B7 , B9 ,B12) which include fruits, vegetables, nuts, grains, beans, and lentils.
In this article you will read:
What is vitamin B and what are its benefits for the body?
Vitamin B is an essential nutrient that the body needs to function properly. It can help the body fight off infections, maintain healthy blood cells, and support the nervous system. It can also help to protect against heart disease and obesity. There are several types of vitamin B:
There are two main types of vitamin B:
water-soluble and fat-soluble. Water-soluble vitamins are found in foods such as leafy green vegetables, fruit, and milk. Fat-soluble vitamins are found in animal products such as eggs, fish, and meat.
Vitamin B is a vital nutrient for everyone to get enough of. Even if you don’t have any health problems, getting enough vitamin B can make you healthier overall.
There are many benefits to getting enough vitamin B in your diet. It can help your body fight off infections and support the nervous system. It can also help to prevent heart disease and obesity.
Vitamin B is a vital vitamin that is needed for many bodily functions. Because vitamin B plays a role in many processes within the body, it can be helpful for a number of different conditions and health concerns.
One of the most well-known benefits of vitamin B is its role in maintaining and improving overall health. Because vitamin B plays important roles in the nervous system, cardiovascular system, and immune system, it can help to support these systems and maintain healthy levels of function.
It is also important to note that vitamin B works with other vitamins and minerals to ensure that they are properly absorbed and utilized by the body. As such, it is important to make sure that you are getting all of your recommended daily amounts of vitamin B.
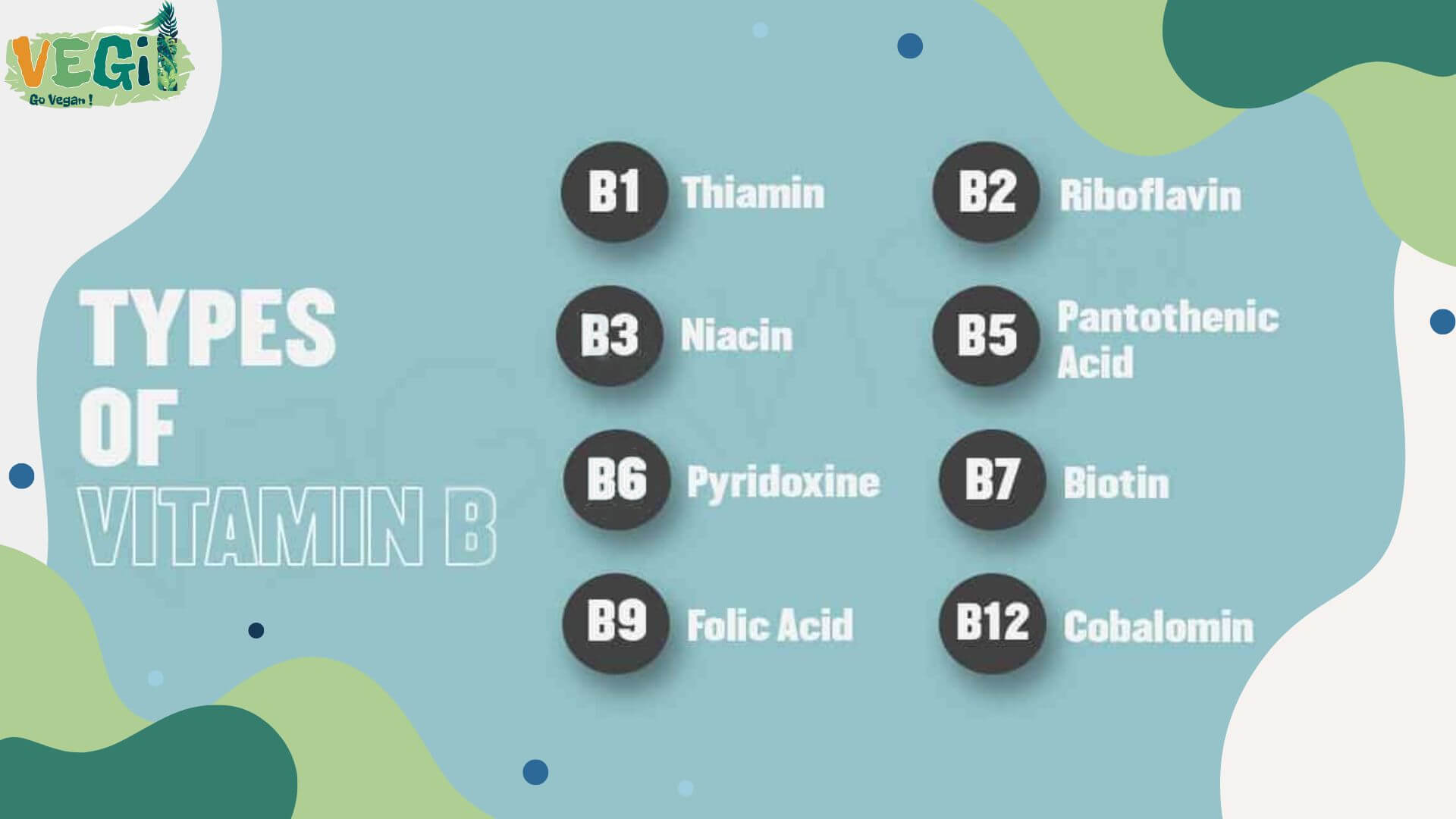
Types of vitamin B and the best herbal sources
Vitamin B1 :
Chronic thiamine deficiency may result from low intake, poor absorption, increased loss (through urination or defecation), or increased requirements (especially during pregnancy).
8 Best Vegetarian Sources of Vitamin B1( Thiamin )
-
- Flax Seeds – Thiamin per 100g 1.6mg (137% DV)
- Parsley -Thiamin per 100g 1mg (87% DV)
- Navy Beans – Thiamin per 100g 0.2mg (20% DV)
- Green Peas – Thiamin per 100g 0.3mg (22% DV)
- Firm Tofu – Thiamin per 100g – 0.2mg (13% DV)
- Brown Rice – Thiamin per 100g 0.2mg (15% DV)
- Acorn Squash – Thiamin per 100g 0.2mg (14% DV)
- Asparagus – Thiamin per 100g 0.2mg (14% DV)
Vitamin B2
5 Best Vegetarian Sources of Vitamin B2( Riboflavin )
1- Fortified Tofu
- Riboflavin per Cup : 1mg (76% DV) 0.4mg
- Riboflavin per 100g : 0.4mg (34% DV)
2- Almonds
- Riboflavin per Cup : 0.3mg (25% DV)
- Riboflavin per 100g :1.1mg (88% DV)
3- Spinach
- Riboflavin per Cup Cooked : 0.4mg (33% DV)
- Riboflavin per 100g : 0.2mg (18% DV)
4- Mushrooms
- Riboflavin per Cup Cooked : 0.5mg (38% DV)
- Riboflavin per 100g : 0.5mg (36% DV)
5-Avocados
- Riboflavin per Avocado : 0.3mg (20% DV)
- Riboflavin per 100g : 0.1mg (10% DV)
Vitamin B3
6 Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin B3( Niacin )
- Peanuts – Niacin per 100g : 14.4mg (90% DV)
- Portabella Mushrooms – Niacin per 100g : 6.3mg (39% DV)
- Sweet Potatoes – Niacin per Cup Mashed 2.4mg (15% DV)
- Avocados – Niacin per Avocado : 3.5mg (22% DV)
- Green Peas – Niacin per Cup Cooked : 3.2mg (20% DV)
- Brown Rice – Niacin per 100g : 2.6mg (16% DV)
5 Vegetarian Sources of Vitamin B5( Pantothenic Acid )
- Shiitake Mushrooms – Vitamin B5 per 100g : 3.6mg (72% DV)
- Avocados – Vitamin B5 per Avocado : 2.8mg (56% DV)
- Sunflower Seeds – Vitamin B5 per 1oz Handful : 2mg (40% DV)
- Sweet Potatoes Vitamin B5 per 100g : 0.5mg (10% DV)
- Lentils – Vitamin B5 per 100g : 0.6mg (13% DV)
6 Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin B6
- Pistachio Nuts – Vitamin B6 per 100g : 1.7mg (100% DV)
- Fortified Tofu – Vitamin B6 per 100g : 0.5mg (29% DV)
- Bananas – Vitamin B6 per 100g : 0.4mg (22% DV)
- Potatoes – Vitamin B6 per 100g : 0.3mg (18% DV)
- Avocados – Vitamin B6 per 100g : 0.3mg (15% DV)
- Sweet Potatoes – Vitamin B6 per 100g : 0.2mg (14% DV)


The daily recommended intake of vitamin B
There is not a set daily vitamin B intake, but the Institute of Medicine recommends two servings of whole grains, 1 serving of vegetables and 2 servings of fruit per day. You can get vitamin B from a variety of whole grains like wheat, millet, oats, barley and quinoa. You can also consume whole-grain bread and cereals, whole-grain pasta, brown rice and popcorn. A good way to get your B is to include these in your diet. Whole-grain products are the richest source of dietary fiber, which is essential for good health but is not a vitamin. They also provide vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. Vitamin B is found in a variety of whole grains and is particularly found in whole-grain bread, cereals and pasta.
Which vegan foods are good sources of vitamin B?
There are a variety of vegan foods that can be good sources of vitamin B. They include:
– Bananas –
Bananas are rich in Vitamin B6 and have many other health benefits too, like being good for your skin, heart and even weight loss! They are also a great source of energy and fuel for your day, so make sure you have one a day.
– Spinach –
Spinach is one of the best vegetables you can consume. It is rich in Vitamin B and also contains high amounts of folate.
– Cucumber –
Cucumbers are a good source of vitamin B and also help in maintaining water balance in the body.
– Vitamin-rich vegan milk –
Vitamin-rich vegan milk like soymilk, oat milk and almond milk are good sources of vitamin B. They are easy to prepare and can be consumed in the morning, during the day or even as a midnight snack.
– Plant-based protein –
Plant-based proteins like tofu, seitan and soy products are rich in vitamin B. It is important to consume protein-rich foods regularly during a healthy diet as it helps in building muscles and maintaining energy levels.
– Vitamin-rich vegan sweeteners –
Vitamin-rich vegan sweeteners like agave, raw cane sugar, date syrup, etc. are good sources of vitamin B. They can be consumed as and when required.
– Nuts –
Nuts are a good source of vitamin B and also contain many minerals like zinc, manganese, selenium and protein. They are easy to consume as they are rich in fat and are healthy to consume.
– Vitamin-rich vegan drinks –
Vitamin-rich vegan drinks like soya or oat-based drinks, kirsch, pomegranate, etc. are also good sources of vitamin B. They can be consumed as and when required.

The Best of Vegan vitamin B foods:
- Nutritional yeast is a vegan source of vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B6, vitamin B9, and vitamin B12.
- Vitamin B1 and vitamin B2 are found in Spirulina Seaweed , Flax Seeds and Dried Sunflower Seeds.
- Vitamin B3, vitamin B5, vitamin B6, and vitamin B9 are found in spinach.
- Vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B3, vitamin B5, and vitamin B6 can be found in sweet potatoes.
- Vitamin B7, vitamin B9, and vitamin B12 can be found in avocados.
40 Plant Sources Rich in Vitamin B1
| Row | Sources rich in vitamin B1 | Vitamin B1 mg/kg) |
| 1 | Dried Spirulina Seaweed | 2.4mg (198% DV) |
| 2 | Flax Seeds | 1.6mg (137% DV) |
| 3 | Dried Sunflower Seeds | 1.5mg (123% DV) |
| 4 | Raw Sesame Butter (Tahini) | 1.3mg (107% DV) |
| 5 | Hemp Seeds | 1.3mg (106% DV) |
| 6 | Dried Pine Nuts | 1.2mg (104% DV) |
| 7 | Macadamia Nuts | 1.2mg (100% DV) |
| 8 | Dried Pilinuts | 0.9mg (76% DV) |
| 9 | Dried Chives | 0.9mg (75% DV) |
| 10 | Dried Hickorynuts | 0.9mg (72% DV) |
| 11 | Pistachio Nuts | 0.9mg (73% DV) |
| 12 | Sesame Seeds (Toasted) | 0.8mg (67% DV) |
| 13 | Dried Japanese Chestnuts | 0.8mg (67% DV) |
| 14 | Dry Roasted Macadamia Nuts | 0.7mg (59% DV) |
| 15 | Dry Roasted Pistachio Nuts | 0.7mg (58% DV) |
| 16 | Pecans | 0.7mg (55% DV) |
| 17 | Hazelnuts | 0.6mg (54% DV) |
| 18 | Dried Lotus Seeds | 0.6mg (53% DV) |
| 19 | Raw Peanuts | 0.6mg (53% DV) |
| 20 | Chia Seeds | 0.6mg (52% DV) |
| 21 | Brazilnuts | 0.6mg (51% DV) |
| 22 | Sun-Dried Tomatoes | 0.5mg (44% DV) |
| 23 | Dry Roasted Pecans | 0.5mg (38% DV) |
| 24 | Tamarinds | 0.4mg (36% DV) |
| 25 | Dried Ginkgo Nuts | 0.4mg (36% DV) |
| 26 | Dry-Roasted Soybeans | 0.4mg (36% DV) |
| 27 | Butternuts | 0.4mg (32% DV) |
| 28 | Kidney Bean Sprouts | 0.4mg (31% DV) |
| 29 | Durian | 0.4mg (31% DV) |
| 30 | Oil Roasted Cashews | 0.4mg (30% DV) |
| 31 | Pine Nuts (Dried) | 0.4mg (30% DV) |
| 32 | Walnuts | 0.3mg (28% DV) |
| 33 | Soybean Sprouts | 0.3mg (28% DV) |
| 34 | Dried Beechnuts | 0.3mg (25% DV) |
| 35 | Shiitake Mushrooms | 0.3mg (25% DV) |
| 36 | Breadfruit Nuts (Seeds) | 0.3mg (24% DV) |
| 37 | Green Peas | 0.3mg (22% DV) |
| 38 | Peas | 0.3mg (22% DV) |
| 39 | Bananas | 0.2mg (15% DV) |
| 40 | Melon Balls | 0.2mg (14% DV) |
1.2mg Thiamin (B1) = 100% DV
43 Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
| Row | Sources rich in vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | Vitamin B2 mg/kg) |
| 1 | Dried Pasilla Peppers | 3.2mg (246% DV) |
| 2 | Parsley | 2.3mg (174% DV) |
| 3 | Dried Ancho Peppers | 2.3mg (173% DV) |
| 4 | Dried Chives | 1.5mg (115% DV) |
| 5 | Dried Shiitake Mushrooms | 1.3mg (98% DV) |
| 6 | Dry Roasted Almonds | 1.2mg (92% DV) |
| 7 | Almonds | 1.1mg (88% DV) |
| 8 | Dried Fungi Cloud Ears | 0.8mg (65% DV) |
| 9 | Dry-Roasted Soybeans | 0.8mg (58% DV) |
| 10 | Dried Litchis | 0.6mg (44% DV) |
| 11 | Raw Sesame Butter (Tahini) | 0.5mg (39% DV) |
| 12 | Raw Cremini Mushrooms | 0.5mg (38% DV) |
| 13 | Sun-Dried Tomatoes | 0.5mg (38% DV) |
| 14 | Cremini Mushrooms | 0.5mg (38% DV) |
| 15 | Dried Longans | 0.5mg (38% DV) |
| 16 | White Button Mushrooms | 0.5mg (36% DV) |
| 17 | Laver Seaweed | 0.4mg (34% DV) |
| 18 | Extra Firm Fortified Tofu | 0.4mg (34% DV) |
| 19 | Safflower Seeds | 0.4mg (32% DV) |
| 20 | Portobellos | 0.4mg (31% DV) |
| 21 | Dried Beechnuts | 0.4mg (29% DV) |
| 22 | Dried Japanese Chestnuts | 0.4mg (29% DV) |
| 23 | Dried Sunflower Seeds | 0.4mg (27% DV) |
| 24 | Oyster Mushrooms | 0.3mg (27% DV) |
| 25 | Kale | 0.3mg (27% DV) |
| 26 | Spirulina | 0.3mg (26% DV) |
| 27 | Hemp Seeds | 0.3mg (22% DV) |
| 28 | Cooked Beet Greens | 0.3mg (22% DV) |
| 29 | Fava Beans (Raw) | 0.3mg (22% DV) |
| 30 | Edamame | 0.3mg (22% DV) |
| 31 | Garden Cress | 0.3mg (20% DV) |
| 32 | Sesame Seeds (Toasted) | 0.3mg (19% DV) |
| 33 | Kidney Bean Sprouts | 0.3mg (19% DV) |
| 34 | Wakame | 0.2mg (18% DV) |
| 35 | Dried Bananas | 0.2mg (18% DV) |
| 36 | Soy Milk | 0.2mg (16% DV) |
| 37 | Dried Peaches | 0.2mg (16% DV) |
| 38 | Durian | 0.2mg (15% DV) |
| 39 | Prunes (Low-Moisture) | 0.2mg (13% DV) |
| 40 | Kelp Seaweed | 0.2mg (12% DV) |
| 41 | Green Soybeans | 0.2mg (12% DV) |
| 42 | Tamarinds | 0.2mg (12% DV) |
| 43 | Dried Apples | 0.2mg (12% DV) |
1.3mg Riboflavin (B2) = 100% DV
58 Vitamin B5 rich foods for vegetarians
| Row | Sources rich in vitamin B5 (Pantothenic) | Vitamin B5 mg/kg) |
| 1 | Enriched Bran Flakes | 29.8mg (596% DV) |
| 2 | Dried Shiitake Mushrooms | 21.9mg (438% DV) |
| 3 | Pepeao Dried | 21.5mg (430% DV) |
| 4 | Rice Bran | 7.4mg (148% DV) |
| 5 | Sunflower Seed | 7.1mg (141% DV) |
| 6 | Sunflower Seed Kernels Oil | 6.9mg (139% DV) |
| 7 | Oatmeal | 6mg (120% DV) |
| 8 | Cereal Barley Dry Fortified | 4.9mg (98% DV) |
| 9 | Safflower Seeds | 4mg (81% DV) |
| 10 | Dried Spirulina Seaweed | 3.5mg (70% DV) |
| 11 | Paprika | 2.5mg (50% DV) |
| 12 | Lentils Raw | 2.1mg (43% DV) |
| 13 | Dried Chives | 2.1mg (42% DV) |
| 14 | Sun-Dried Tomatoes | 2.1mg (42% DV) |
| 15 | Soy Meal Defatted Raw | 2mg (40% DV) |
| 16 | Radishes Oriental Dried | 1.9mg (37% DV) |
| 17 | Raw Peanuts | 1.8mg (35% DV) |
| 18 | Black Walnuts (Dried) | 1.7mg (33% DV) |
| 19 | Mothbeans Mature Seeds Raw | 1.5mg (31% DV) |
| 20 | White Button Mushrooms | 1.5mg (30% DV) |
| 21 | Cowpeas Mature Seeds | 1.5mg (30% DV) |
| 22 | Cremini Mushrooms | 1.5mg (30% DV) |
| 23 | Avocados | 1.4mg (28% DV) |
| 24 | Dried Spearmint | 1.4mg (28% DV) |
| 25 | Black Pepper | 1.4mg (28% DV) |
| 26 | Toasted Wheat Germ | 1.4mg (28% DV) |
| 27 | Shallots Freeze-Dried | 1.4mg (28% DV) |
| 28 | Enoki Mushrooms | 1.4mg (27% DV) |
| 29 | Oyster Mushrooms | 1.3mg (26% DV) |
| 30 | Mushrooms Portobellos | 1.3mg (25% DV) |
| 31 | Stirfried Soybean Sprouts | 1.2mg (24% DV) |
| 32 | Dry-Roasted Cashews | 1.2mg (24% DV) |
| 33 | Cashew Butter | 1.2mg (24% DV) |
| 34 | Cereals Oats Instant Fortified Plain Dry | 1.2mg (24% DV) |
| 35 | Chicory Greens | 1.2mg (23% DV) |
| 36 | Cereals Oats Regular And Quick Not Fortified Dry | 1.1mg (22% DV) |
| 37 | Curry Powder | 1.1mg (21% DV) |
| 38 | Low-Moisture Dried Apricots | 1.1mg (21% DV) |
| 39 | Dried Parsley | 1.1mg (21% DV) |
| 40 | Pea Sprouts | 1mg (21% DV) |
| 41 | Flax Seeds | 1mg (20% DV) |
| 42 | Dry Roasted Peanuts | 1mg (20% DV) |
| 43 | Dried Beechnuts | 0.9mg (19% DV) |
| 44 | Acorns (Dried) | 0.9mg (19% DV) |
| 45 | Soybean Sprouts | 0.9mg (19% DV) |
| 46 | Dried Oregano | 0.9mg (18% DV) |
| 47 | Chili Powder | 0.9mg (18% DV) |
| 48 | Hazelnuts | 0.9mg (18% DV) |
| 49 | Beans Black Mature Seeds Raw | 0.9mg (18% DV) |
| 50 | Baked Sweet Potatoes | 0.9mg (18% DV) |
| 51 | Grape Nuts Cereal | 0.9mg (17% DV) |
| 52 | Beans Kidney Royal Red Mature Seeds Raw | 0.8mg (16% DV) |
| 53 | Parsnips | 0.6mg (12% DV) |
| 54 | Lentil Sprouts | 0.6mg (12% DV) |
| 55 | Plantains Cooked | 0.5mg (11% DV) |
| 56 | Broccoli | 0.6mg (11% DV) |
| 57 | Dried Peaches | 0.6mg (11% DV) |
| 58 | Dried Apricots | 0.5mg (10% DV) |
5mg Pantothenic acid (B5) = 100% DV
45 Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin B9 (Folate)
| Row | Sources rich in vitamin B9 (Folate) | Vitamin B9 mg/kg) |
| 1 | Arrowroot | 338mcg (85% DV) |
| 2 | Edamame | 311mcg (78% DV) |
| 3 | Dried Sunflower Seeds | 227mcg (57% DV) |
| 4 | Spinach | 194mcg (49% DV) |
| 5 | Wakame | 196mcg (49% DV) |
| 6 | Turnip Greens | 194mcg (49% DV) |
| 7 | Freeze-Dried Parsley | 194mcg (49% DV) |
| 8 | Lentils | 181mcg (45% DV) |
| 9 | Kelp Seaweed | 180mcg (45% DV) |
| 10 | Soybean Sprouts | 172mcg (43% DV) |
| 11 | Dried Shiitake Mushrooms | 163mcg (41% DV) |
| 12 | Safflower Seeds | 160mcg (40% DV) |
| 13 | Parsley | 152mcg (38% DV) |
| 14 | Asparagus (Cooked) | 149mcg (37% DV) |
| 15 | Asparagus | 149mcg (37% DV) |
| 16 | Pea Sprouts | 144mcg (36% DV) |
| 17 | Endive | 142mcg (36% DV) |
| 18 | Cooked Catjang Beans | 142mcg (36% DV) |
| 19 | Navy Beans | 140mcg (35% DV) |
| 20 | Cooked Small White Beans | 137mcg (34% DV) |
| 21 | Romaine Lettuce | 136mcg (34% DV) |
| 22 | Lettuce | 136mcg (34% DV) |
| 23 | Collards | 129mcg (32% DV) |
| 24 | Kidney Beans | 130mcg (33% DV) |
| 25 | Cooked Blackeyed Peas | 127mcg (32% DV) |
| 26 | Adzuki Beans | 121mcg (30% DV) |
| 27 | Acorns (Dried) | 115mcg (29% DV) |
| 28 | Cooked Green Soybeans | 111mcg (28% DV) |
| 29 | Dried Beechnuts | 113mcg (28% DV) |
| 30 | Hemp Seeds | 110mcg (28% DV) |
| 31 | Dried Chinese Chestnuts | 110mcg (28% DV) |
| 32 | Hazelnuts | 113mcg (28% DV) |
| 33 | Dried Japanese Chestnuts | 109mcg (27% DV) |
| 34 | Broccoli | 108mcg (27% DV) |
| 35 | Dried Ginkgo Nuts | 106mcg (27% DV) |
| 36 | Broad Beans (Fava) | 104mcg (26% DV) |
| 37 | Dried Lotus Seeds | 104mcg (26% DV) |
| 38 | Sesame Seeds (Toasted) | 98mcg (25% DV) |
| 39 | Raw Sesame Butter (Tahini) | 98mcg (25% DV) |
| 40 | Walnuts | 98mcg (25% DV) |
| 41 | Flax Seeds | 87mcg (22% DV) |
| 42 | Avocados | 81mcg (20% DV) |
| 43 | Mangos | 43mcg (11% DV) |
| 44 | Sweet Corn | 42mcg (11% DV) |
| 45 | Oranges | 30mcg (8% DV) |
In this article “Vitamin B rich foods for vegetarians” I have tried to give you the most complete information about plant sources of vitamin B. If you are a vegan or vegetarian, you can supply the B vitamins your body needs with a balanced and planned diet of vegetables, fruits, and plant sources, and if you are deficient in B vitamins, you can use vegan B complex supplements.
If you have any questions or comments, please give me feedback below this article. I will try to update this article monthly and introduce you to more plant sources of vitamin B.











