Vitamin E Rich Foods for Vegetarians
Plant based sources of Vitamin E

How to Get Your Vitamin E Routine At Its Best – Find The Best Vegan & Vegetarian Vitamin E Rich Foods – Vitamin E Rich Foods for Vegetarians: Perfect for You, Your Family and Your Health!
The diverse range of vitamin E-rich foods on the market today make it easier than ever before to get this essential nutrient into your diet. This article walks you through everything you need to know about getting vitamin E in your diet. Keep reading to learn more!
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that helps control blood sugar and promote healthy skin. It can be found in foods such as nuts, oils, and wheat germ.
Vitamin E is needed to keep cell membranes safe from oxidative damage. It also plays an important role in immune function and the synthesis of cellular substances. And since it’s also been shown to lower the risk of heart disease.
Vitamin E is an important vitamin that is responsible for many functions in your body. These include supporting cell growth and maintenance, as well as protecting against oxidative stress and maintaining healthy endothelial function. A deficiency in vitamin E is rare, but if it does occur it can have a significant impact on your health.
In this article we will explore the top sources of vitamin E in a vegetarian diet and its effect on health and we will explore the top 10 foods rich in vitamin E, as well as tips for getting enough of this essential nutrient if you are a vegetarian.
The diverse range of vitamin E-rich foods on the market today make it easier than ever before to get this essential nutrient into your diet. This article walks you through everything you need to know about getting vitamin E in your diet. Keep reading to learn more!
In this article you will read:
What is Vitamin E?
Like many other nutrients, vitamin E is a group of compounds. The most important vitamin E is called α-tocopherol and is the form found in plants and animals. While vitamin E is found in a wide variety of foods, the most important dietary sources are oils, nuts, and seeds. Vitamin E is fat-soluble, and since the body only stores a small amount of it, we need to take it with each meal. Foods rich in vitamin E include: – Sunflower seeds – Rapeseed oil – Sesame seeds – Pine seeds – Walnuts – Vitamin E is fat-soluble and is stored in our body as fat. We do not store much vitamin E in our body though, and if you do not get enough, you will experience symptoms like: – Decreased immunity – Wrinkles – Dry skin
Types of Vitamin E
There are two types of vitamin E: α-tocopherol and γ-tocopherol.
These compounds have very similar functions in the body, but some studies have suggested that α-tocopherol may have better immunity and prevention of certain diseases. α-Tocopherol is found in high amounts in oils such as sunflower and rapeseed oil, while γ-tocopherol is only found in some fruits and vegetables and soybeans.
Why Is Vitamin E Important?
Vitamin E is important because it is an important antioxidant that helps fight free radicals that can lead to damage to cells and DNA in the body. Vitamin E is not a vitamin for the body to make its own, but rather it is a vitamin that the body needs and gets from food. Vitamin E is an antioxidant that is important in helping the body fight harmful free radicals. When we eat food, the food is broken down in the stomach and the various components are absorbed. Vitamin E is fat soluble, and as such, it is easily absorbed by the body. Free radicals are oxygen molecules that are naturally produced in the body and are also present in the environment and in food. Antioxidants are molecules that fight off free radicals, and vitamin E is one of these antioxidants.
Tried-and-true ways to get your daily vitamin E
– Eat a diet high in fresh vegetables and fruits – Vitamin E is found in many vegetables and fruits. Some examples include: – Bananas – Raspberries – Peppers – Nuts – Dark green vegetables – Beans – Avocado – Sunflower seeds – Oats – Flaxseeds – Vitamin E is fat soluble, so make sure you consume a lot of fat with your meals. A diet high in fresh vegetables and fruits is a great way to get your daily vitamin E. Vitamin E is found in many vegetables and fruits. Some examples include: – Bananas – Raspberries – Peppers – Nuts – Dark green vegetables – Beans – Avocado – Sunflower seeds – Oats – Flaxseeds – Vitamin E is fat soluble, so make sure you consume a lot of fat with your meals.
Good vegan sources of vitamin E
Vitamin E is fat soluble and is only found in a few plant foods. Avocado is one of the best plant-based sources of vitamin E, and it is also delicious!
All other vegetable and fruit sources of vitamin E are found in trace amounts – avocados contain up to 1200 IU!
You can also add avocado to your salads, smoothies or make guacamole.
Avocado is one of the best plant-based sources of vitamin E.
Bad vegan sources of vitamin E
– Soymilk –
Soymilk contains a similar vitamin E compound to that of nuts, but at a much lower amount. At most, you will receive 30% of the daily value of vitamin E in one cup of soya milk.
Soymilk is a good vegan source of calcium and protein, but vitamin E is not present in more than trace amounts.
When looking at the daily values, you will find that the vitamin E value is only a tiny fraction of that found in other plant-based foods.
The Good News About Vitamin E and Vegetarians
– Fewer Disease Risk Factors –
Vitamin E has been shown in studies to be related to better health, lowered disease risk factors and lowered rates of cancer. Studies have shown that people who eat a diet rich in vitamin E have fewer disease risk factors and lower rates of cancer, and this is partly due to the antioxidant protection of vitamin E. Studies have also found a link between a diet high in fruits and vegetables and lower blood pressure. Vitamin E has been shown to be related to better health, lowered disease risk factors and lowered rates of cancer and this is partly due to the antioxidant protection of vitamin E.
3 vegan foods rich in vitamin E
– Sunflower seeds –
This is the richest vegan source of vitamin E. One cup of sunflower seeds contains 56% of your daily value of vitamin E. Sunflower seeds are an excellent source of vitamin E, containing over 56% of the daily value per one-cup serving. They are also high in iron, magnesium, and protein, making them an all-around powerful plant-based source of nutrition. Vitamin E is fat soluble, so make sure you consume a lot of fat with your meals. Sunflower seeds are an excellent source of vitamin E, containing over 56% of the daily value per one-cup serving. They are also high in iron, magnesium, and protein, making them an all-around powerful plant-based source of nutrition.
– Sesame seeds –
This seed, which is similar in taste to flaxseeds or olives, is also a great source of vitamin E at 28% of the daily value per one-cup serving. Sesame seeds are a great source of vitamin E, containing 28% of the daily value per one-cup serving. They are also high in iron, magnesium, and protein, making them an all-around powerful plant-based source of nutrition. Vitamin E is fat soluble, so make sure you consume a lot of fat with your meals. Sesame seeds are a great source of vitamin E, containing 28% of the daily value per one-cup serving. They are also high in iron, magnesium, and protein, making them an all-around powerful plant-based source of nutrition.
– Rapeseed oil –
This oil is rich in vitamin E and is a good alternative to sunflower oil. One tablespoon of rapeseed oil contains 30% of your daily value of vitamin E. Rapeseed oil is one of the richest oils in vitamin E. One tablespoon of rapeseed oil contains over 30% of your daily value of vitamin E. It is also high in omega-3 fatty acids and is typically not hydrogenated, making it a very good choice for vegans. Vitamin E is fat soluble, so make sure you consume a lot of fat with your meals. Rapeseed oil is one of the richest oils in vitamin E. One tablespoon of rapeseed oil contains over 30% of your daily value of vitamin E. It is also high in omega-3 fatty acids and is typically not hydrogenated, making it a very good choice for vegans.
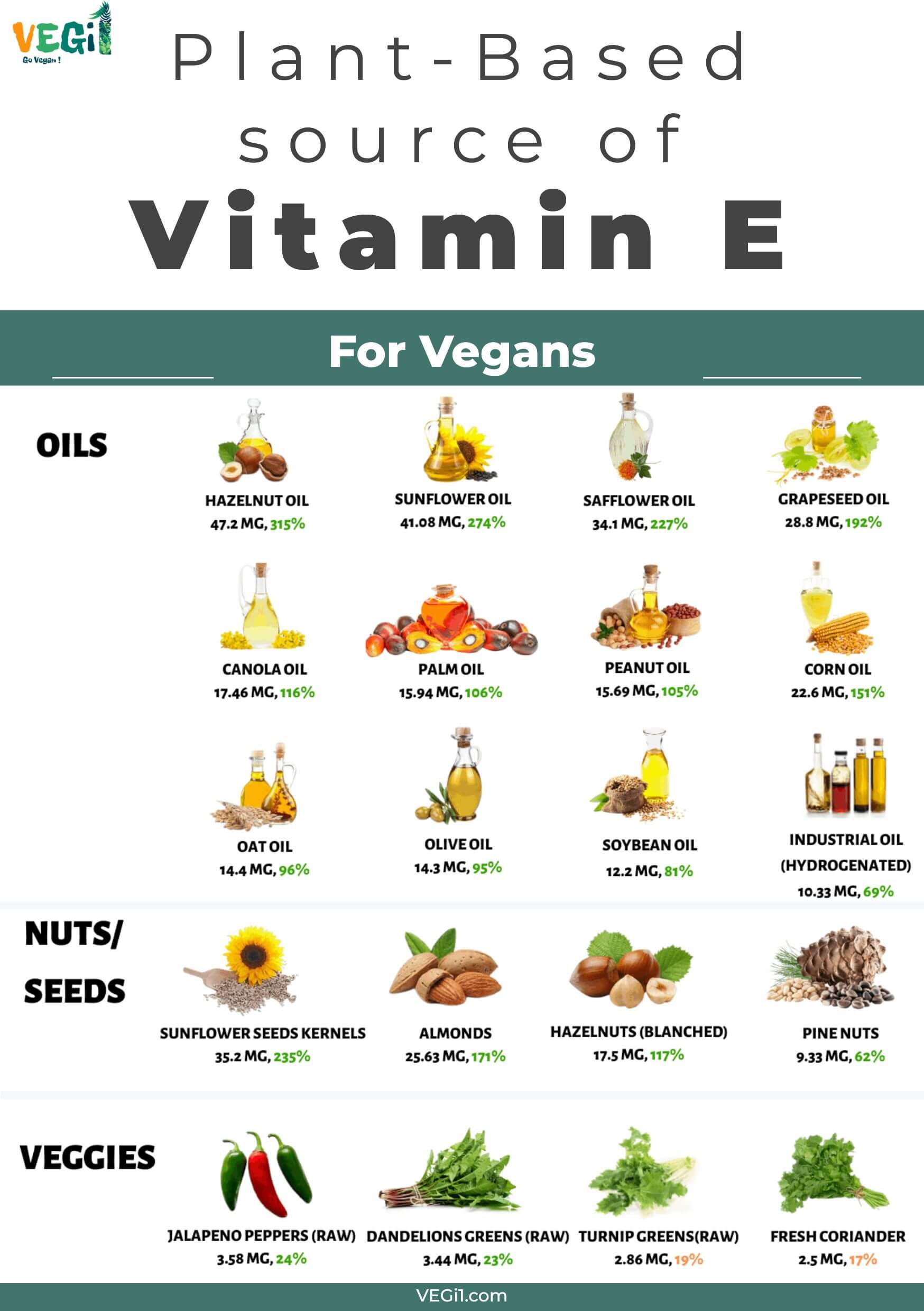
10 Nuts and Seeds Rich in Vitamin E for Vegetarians
| Nuts rich in Vitamin E | Vitamin E mg/kg) |
| Dried Sunflower Seeds | 35.2mg (234% DV) |
| Almonds | 25.6mg (171% DV) |
| Almond Butter | 24.2mg (161% DV) |
| Hazelnuts | 15mg (100% DV) |
| Pine Nuts | 9.3mg (62% DV) |
| Brazilnuts | 5.7mg (38% DV) |
| Dry Roasted Peanuts | 4.9mg (33% DV) |
| Pistachio Nuts | 2.9mg (19% DV) |
| Dried Pumpkin And Squash Seeds | 2.2mg (15% DV) |
| Black Walnuts | 2.1mg (14% DV) |
source : myfooddata

16 Fruits Highest in Vitamin E for vegans and vegetarians
Note: Ranked by a 100 gram Serving Size , 15mg Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol) = 100% DV
- Dried Apricots – 4.3mg (29% DV)
- Mango – 4mg (27% DV)
- Green Olives – 3.8mg (25% DV)
- Avocados – 2.7mg (18% DV)
- Dried Blueberries – 2.4mg (16% DV)
- Mamey Sapote – 2.1mg (14% DV)
- Kiwifruit – 1.5mg (10% DV)
- Cranberries – 1.3mg (9% DV)
- Blackberries – 1.2mg (8% DV)
- European Black Currants – 1mg (7% DV)
- Raspberries – 0.9mg (6% DV)
- Apricots- 0.9mg (6% DV)
- Mulberries – 0.9mg (6% DV)
- Nectarines – 0.8mg (5% DV)
- Yellow Peaches – 0.7mg (5% DV)
- Guavas – 0.7mg (5% DV)
source : myfooddata
Vegetables Highest in Vitamin E (Alpha-Tocopherol)
| Vegetables rich in Vitamin E | Vitamin E mg/kg) |
| Dried Spirulina Seaweed | 5mg (33% DV) |
| Canned Tomato Paste | 4.3mg (29% DV) |
| Jalapeno Peppers | 3.6mg (24% DV) |
| Dandelion Greens | 3.4mg (23% DV) |
| Red Bell Peppers | 3.1mg (21% DV) |
| Sun-Dried Hot Chile Peppers | 3.1mg (21% DV) |
| Turnip Greens | 2.9mg (19% DV) |
| Cilantro | 2.5mg (17% DV) |
| Broccoli Raab | 2.5mg (17% DV) |
| Dandelion Greens | 2.4mg (16% DV) |
| Taro | 2.4mg (16% DV) |
| Chicory Greens | 2.3mg (15% DV) |
| Radicchio | 2.3mg (15% DV) |
| Collards | 2.3mg (15% DV) |
| Spinach | 2.1mg (14% DV) |
| Mustard Greens | 2mg (13% DV) |
| Canned Tomato Puree | 2mg (13% DV) |
| Swiss Chard | 1.9mg (13% DV) |
| Turnip Greens | 1.9mg (13% DV) |
| Mustard Greens | 1.8mg (12% DV) |
| Beet Greens | 1.8mg (12% DV) |
| Boiled Red Bell Peppers | 1.7mg (11% DV) |
| Kale | 1.6mg (11% DV) |
| Sweet Red Bell Peppers | 1.6mg (11% DV) |
| Broccoli Raab (Rapini) | 1.6mg (11% DV) |
| Beet Greens | 1.5mg (10% DV) |
| Asparagus | 1.5mg (10% DV) |
| Green Bell Peppers | 1.4mg (9% DV) |
| Butternut Squash | 1.4mg (10% DV) |
source : myfooddata
9 Beans and Lentils Highest in Vitamin E for vegetarians
- Fortified Silken Tofu – 4.8mg (32% DV) in 1/5 package
- Raw Peanuts – 2.4mg (16% DV) in 1 oz
- Canned Navy Beans – 2mg (14% DV) in 1 cup
- Large White Beans – 1.7mg (11% DV) in 1 cup
- Black Turtle Beans – 1.6mg (11% DV) in 1 cup
- Pinto Beans – 1.6mg (11% DV) in 1 cup
- Fava Beans – 1.5mg (10% DV) in 1 cup
- Black Beans – 1.5mg (10% DV) in 1 cup
- Edamame – 1.1mg (7% DV) in 1 cup
source : myfooddata
I want to tell you is that numbers are not important, as long as you eat fresh fruits and vegetables as much as possible and keep variety in your diet.
In this article” Vitamin E Rich Foods Vegetarian” , I tried to introduce you sources rich in vegetable vitamin E. Please write me any feedback you have in the comments below this article.
FAQ
What are some sources of vitamin E?
Vitamin E is a vitamin that is important for the health of your cells, tissues, and organs. It plays a role in the structure and function of your cells.
There are many sources of vitamin E, including vegetables and fruits, nuts and seeds, and meats. Here are some of the most common sources:
• Bananas
• Raspberries
• Peppers
• Nuts and seeds
• Avocados
• Broccoli
• Sweet Potato
• Lentils
Some of the health benefits associated with vitamin E include:
• Reduces risk of heart disease
• May help maintain healthy bones
• May help lower blood pressure
• May help maintain healthy skin and hair
• Helps build strong muscles Vitamin E may also benefit your cardiovascular system by improving blood coagulation, which helps to prevent events such as heart attacks.
•Reducing homocysteine levels may also be helpful in preventing cardiovascular disease. Low homocysteine can be caused by not having enough vitamin B6 in your diet.
What are the cheapest Plant-based sources of vitamin E?
– Leafy greens such as kale, Swiss chard, and spinach are a good source of vitamin E.
– Tofu is a good source of vitamin E.
– Plantains are a good source of vitamin E.










